Introduction: Why SQL Triggers are Important
SQL triggers are powerful tools that every DBA and developer dealing with databases should understand. In particular, these triggers allow you to specify SQL actions that execute automatically when specific events occur within the database. For instance, you can configure a trigger to update a record in one table whenever a record is inserted into another table.
In this article, you will learn what SQL triggers are, how they work, and how to use them in your database. By following this guide, you will soon become an expert on triggers (päästikute) in SQL!
What Is a Trigger in SQL?
A trigger is a database object that contains SQL logic and executes automatically when a specific database event occurs. To clarify, it activates in response to particular events, making it an efficient method for automating certain database actions.
Moreover, SQL triggers generally associate with specific tables. Consequently, when a table is deleted, all associated triggers are also removed. Thus, an SQL trigger can be invoked before or after the following events:
- INSERT: This event occurs when a new row is added to the table.
- UPDATE: This action takes place when an existing row in the table is modified.
- DELETE: This event occurs when a row in the table is removed.
How Triggers Work in SQL
Whenever an INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE SQL query executes, the RDBMS automatically handles the firing of the corresponding trigger. This process not only helps maintain data integrity but also ensures that necessary actions occur consistently.
For example, triggers can enforce business rules or maintain audit trails without additional coding effort. As a result, they streamline the overall management of database operations.
Benefits of Using SQL Triggers
In addition, SQL triggers provide several advantages that enhance database functionality. Firstly, they automate routine tasks, which minimizes human error. Secondly, they ensure that data remains consistent across related tables, thereby improving data integrity.
Furthermore, triggers can help with auditing changes by logging actions that occur in the database. Consequently, they serve as a valuable tool for tracking data modifications over time.
Conclusion
In summary, SQL triggers are essential components of effective database management. By implementing these automated actions, you can enhance the functionality and reliability of your database systems, leading to more efficient operations and improved application performance.
CREATE DATABASE trigerTARpv23;
USE trigerTARpv23;
--loome tabeli
CREATE TABLE toode(
toodeId int primary key identity (1,1),
toodeNimi varchar(50),
hind int);
--loome tabeli, mis täidab triger
CREATE TABLE logi(
id int primary key identity (1,1),
kasutaja varchar(100),
kuupaev datetime,
sisestatudAndmed text);
Insert trigger – a trigger that tracks the inclusion of data in a table and makes a log in the table of the corresponding entry
--LISAMINE
create trigger toodeLisamine
on toode -- tabel mis jälgitakse
for insert
as
insert into logi(kasutaja, kuupaev, sisestatudAndmed)
select
user,
getdate(),
concat('lisatud andmed', inserted.toodeNimi, ', ', inserted.hind)
from inserted
--kontroll
--kontrollimiseks lisame toode
INSERT INTO toode(toodenimi, hind)
VALUES ('magus õun', 10);
SELECT * FROM toode;
SELECT * FROM logi;

--KUSTUTAMINE
create trigger toodeKustutamine
on toode -- tabel mis jälgitakse
for DELETE
as
insert into logi(kasutaja, kuupaev, sisestatudAndmed)
select
user,
getdate(),
concat('kustutatud andmed', deleted.toodeNimi, ', ', deleted.hind)
from deleted
--kontroll
--kontrollimiseks kustutame toode tabelis toode
DELETE FROM toode
WHERE toodeId=1;
SELECT * FROM toode;
SELECT * FROM logi;

--Uuendamine
create trigger toodeUuendamine
on toode -- tabel mis jälgitakse
for UPDATE
as
insert into logi(kasutaja, kuupaev, sisestatudAndmed)
select
user,
getdate(),
concat('vanad andmed: ', deleted.toodeNimi, ', ', deleted.hind, ' Uued andmed: ', inserted.toodenimi, ', ', inserted.hind)
from deleted INNER JOIN inserted
ON deleted.toodeId=inserted.toodeId
--kontroll
--kontrollimiseks uuendame toode
SELECT * FROM toode;
UPDATE toode SET toodeNimi='orange melon'
WHERE toodeId=2;
SELECT * FROM toode;
SELECT * FROM logi;

SQL Server CREATE TRIGGER example
1) Create a table for logging the changes
CREATE DATABASE production;
USE production;
--1) Create a table for logging the changes
CREATE TABLE product_audits(
change_id INT IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
product_id INT NOT NULL,
product_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
brand_id INT NOT NULL,
category_id INT NOT NULL,
model_year SMALLINT NOT NULL,
list_price DEC(10,2) NOT NULL,
updated_at DATETIME NOT NULL,
operation CHAR(3) NOT NULL,
CHECK(operation = 'INS' or operation='DEL')
);
-- CATEGORIES
CREATE TABLE categories (
category_id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
category_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL
);
-- BRANDS
CREATE TABLE brands (
brand_id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
brand_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL
);
-- PRODUCTS
CREATE TABLE products (
product_id INT IDENTITY (1, 1) PRIMARY KEY,
product_name VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL,
brand_id INT NOT NULL,
category_id INT NOT NULL,
model_year SMALLINT NOT NULL,
list_price DECIMAL (10, 2) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (category_id)
REFERENCES categories (category_id)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (brand_id)
REFERENCES brands (brand_id)
ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE
);
2) Creating an after DML trigger
--2) Creating an after DML trigger
CREATE TRIGGER trg_product_audit
ON products
AFTER INSERT, DELETE
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
INSERT INTO product_audits(
product_id,
product_name,
brand_id,
category_id,
model_year,
list_price,
updated_at,
operation
)
SELECT
i.product_id,
product_name,
brand_id,
category_id,
model_year,
i.list_price,
GETDATE(),
'INS'
FROM
inserted i
UNION ALL
SELECT
d.product_id,
product_name,
brand_id,
category_id,
model_year,
d.list_price,
GETDATE(),
'DEL'
FROM
deleted d;
END
--kontroll
INSERT INTO categories (category_name) VALUES ('Electronica');
INSERT INTO brands (brand_name) VALUES ('Brand');
INSERT INTO products(
product_name,
brand_id,
category_id,
model_year,
list_price
)
VALUES (
'Test product',
1,
1,
2018,
599
);
SELECT * FROM product_audits;
DELETE FROM products WHERE product_id = 322;
SELECT * FROM product_audits;

XAMPP trigerid
TOODE LISAMINE

insert into logi(kasutaja, kuupaev, sisestatudAndmed)
VALUES (
user (),
NOW(),
concat('lisatud andmed', NEW.toodeNimi, ', ', NEW.hind))
INSERT INTO toode(toodenimi, hind)
VALUES ('magus õun', 10);
SELECT * FROM toode;
SELECT * FROM logi;


DESCRIPTION OF PRODUCTS

insert into logi(kasutaja, kuupaev, sisestatudAndmed)
VALUES (
user (),
NOW(),
concat('kustutatud andmed', OLD.toodeNimi, ', ', OLD.hind))
DELETE FROM toode
WHERE toodeId=1;
SELECT * FROM toode;
SELECT * FROM logi;

FUTURE OF PRODUCTS

insert into logi(kasutaja, kuupaev, sisestatudAndmed)
VALUES (
user (),
NOW(),
concat('vanad andmed: ', OLD.toodeNimi, ', ', OLD.hind, ' Uued andmed: ', NEW.toodenimi, ', ', NEW.hind))


Task “animals”
Database name – loomadAndmebaas
--LOOMADANDMEBAAS
CREATE DATABASE loomadAndmebaas;
USE loomadAndmebaas;

Tabelinimi, andmete sisestamiseks ja väljade nimed tabelis, nt. Loo tabel loomad (id, loomaliik ,nimi, vanus, värv)
--LOOMAD
CREATE TABLE loomad(
id int primary key identity (1,1),
loomaliik varchar(50),
nimi varchar(50),
vanus int,
varv varchar(50));
Loo tabel trigerite töö salvestamiseks. Näiteks tabel logi (logiID, kuupaev, andmed, kasutaja)
--loome tabeli, mis täidab triger
CREATE TABLE logi(
logiID int primary key identity(1,1),
kasutaja varchar(100),
kuupaev datetime,
andmed text);

Trigerinimed ja mida triger peab tegema seoses eelnevalt loodud tabeliga (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
INSERT
--INSERT
create trigger loomadLisamine
on loomad
for insert
as
insert into logi(kasutaja, kuupaev, andmed)
select
user,
getdate(),
concat('lisatud andmed', inserted.loomaliik, ', ', inserted.nimi, ', ', inserted.vanus, ', ', inserted.varv)
from inserted
SELECT * FROM logi;
UPDATE
--UPDATE
create trigger loomadUuendamine
on loomad
for UPDATE
as
insert into logi(kasutaja, kuupaev, andmed)
select
user,
getdate(),
concat('vanad andmed: ', deleted.loomaliik, ', ', deleted.nimi, ', ', deleted.vanus, ', ', deleted.varv, ' Uued andmed: ',inserted.loomaliik, ', ', inserted.nimi, ', ', inserted.vanus, ', ', inserted.varv)
from deleted INNER JOIN inserted
ON deleted.id=inserted.id
SELECT * FROM logi;
DELETE
--DELETE
create trigger loomadKustutamine
on loomad
for DELETE
as
insert into logi(kasutaja, kuupaev, andmed)
select
user,
getdate(),
concat('kustutatud andmed',deleted.loomaliik, ', ', deleted.nimi, ', ', deleted.vanus, ', ', deleted.varv)
from deleted
Kasutajanimi, kes saab töötada ainult varem loodud tabeliga (Kasutajanimi – loomaarst. Parool – 12345)


Kasutaja õigused
GRANT INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE ON loomad TO loomaarst;
Kasutajaõiguste kontroll
INSERT
SELECT * FROM loomad
INSERT INTO loomad(loomaliik, nimi, vanus, varv)
VALUES ('karu', 'Valeria', 1, 'valge'),
('ahv', 'Bob', 2, 'prune'),
('delfiin', 'Roxy', 5, 'sinine'),
('kass', 'Murzik', 3, 'punakollane'),
('koer', 'Dobi', 4, 'valge');

UPDATE
SELECT * FROM loomad;
UPDATE loomad SET varv ='pruun'
WHERE id=5;
SELECT * FROM loomad;

DELETE
DELETE FROM loomad
WHERE id =1;
SELECT * FROM loomad;

Kasutajaõiguste kontroll tabelile logi

LOGI tabeli käivitamine

XAMPP
Andmebaasinimi – loomadAndmebaas
Tabelinimi, andmete sisestamiseks ja väljade nimed tabelis, nt. Loo tabel loomad (id, loomaliik ,nimi, vanus, värv)

Loo tabel trigerite (Päästikute) töö salvestamiseks. Näiteks tabel logi (logiID, kuupaev, andmed, kasutaja)


Trigerinimed ja mida triger peab tegema seoses eelnevalt loodud tabeliga (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
LOOMAD LISAMINE

LOOMAD UUENDAMINE
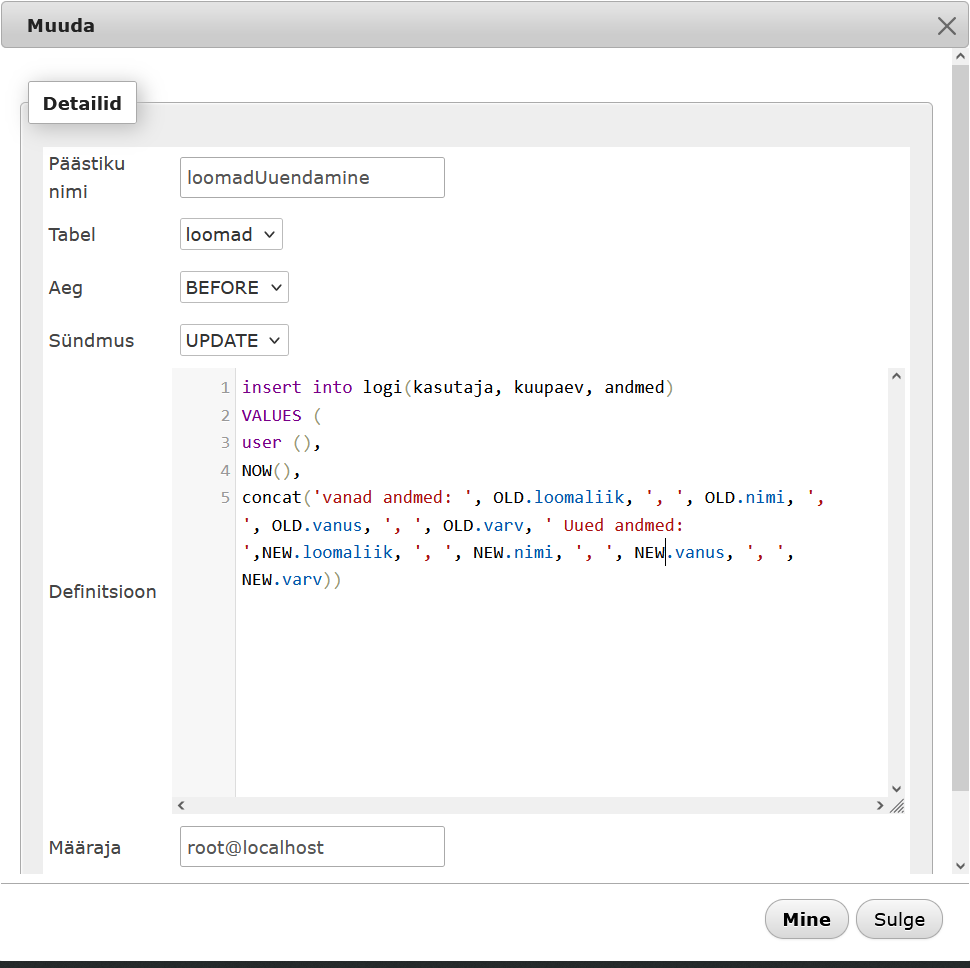
LOOMAD KUSTUTAMINE


Kasutajanimi, kes saab töötada ainult varem loodud tabeliga (Kasutajanimi – loomaarst. Parool – 12345)



Kasutajaõiguste kontroll
INSERT


UPDATE
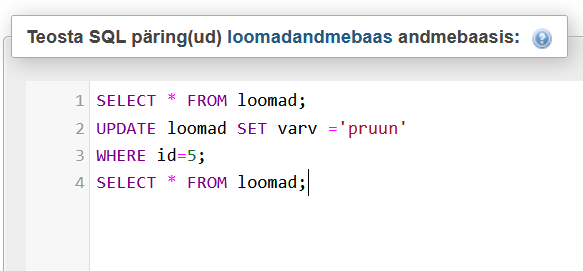
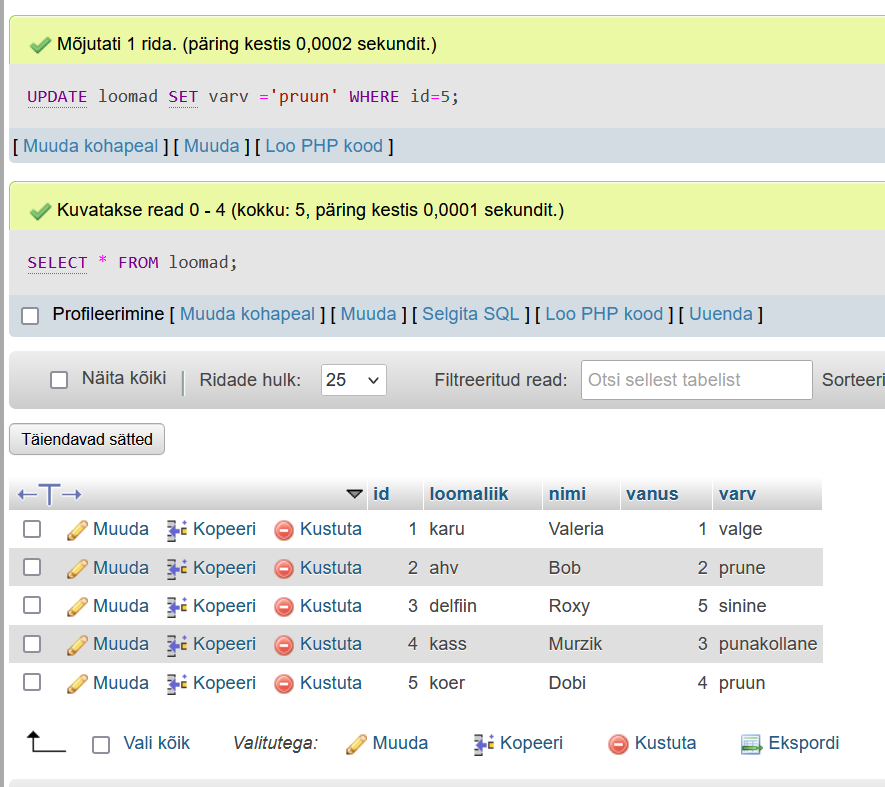
DELETE
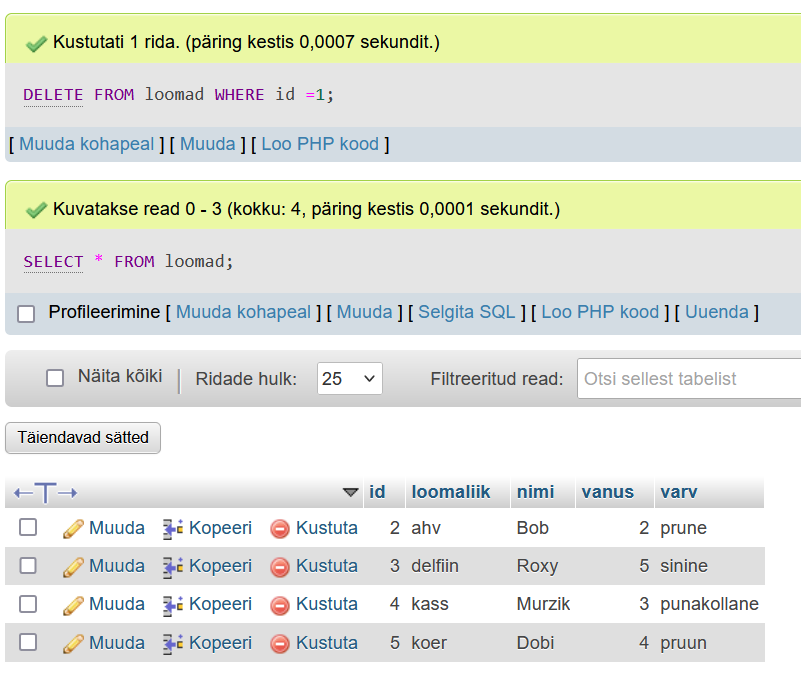
Kasutajaõiguste kontroll tabelile logi (Kasutajanimi – loomaarst)
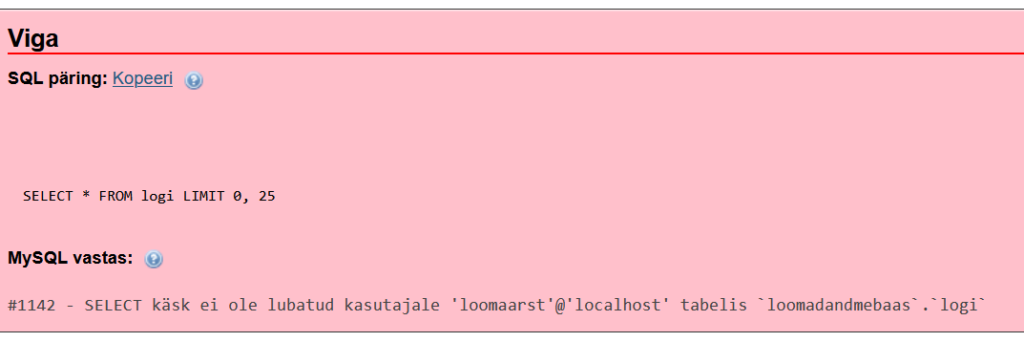
LOGI tabeli käivitamine
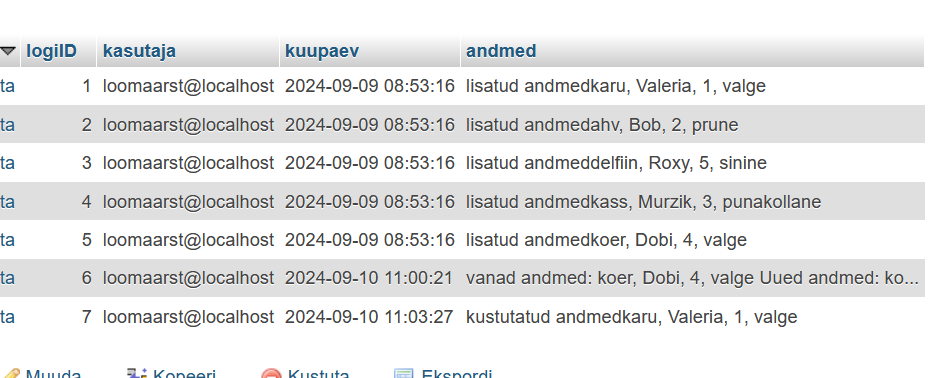
SQL Server Trigerid kahe seotud tabelite põhjal
CREATE DATABASE loomadAndmebaas;
USE loomadAndmebaas;
--LOOMAD
CREATE TABLE loomad(
id INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1),
loomaliik VARCHAR(50),
nimi VARCHAR(50),
vanus INT,
varv VARCHAR(50)
);
INSERT INTO loomad (loomaliik, nimi, vanus, varv)
VALUES ('karu', 'Valeria', 1, 'valge'),
('ahv', 'Bob', 2, 'prune');
--LOGI
CREATE TABLE logi(
id INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1),
aeg DATETIME,
toiming VARCHAR(100),
kasutaja VARCHAR(200),
andmed TEXT
);
--OMANIK
CREATE TABLE omanik(
omanikID INT PRIMARY KEY IDENTITY(1,1),
nimi VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE,
perekonnanimi VARCHAR(50),
sunniaeg DATE
);
INSERT INTO omanik (nimi, perekonnanimi, sunniaeg)
VALUES ('Daria', 'Halchenko', '2006-10-06'),
('Valeria', 'Allik', '2006-03-25');
ALTER TABLE loomad ADD omanikID int;
ALTER TABLE loomad ADD CONSTRAINT fk_omanik
FOREIGN KEY (omanikID) REFERENCES omanik(omanikID);
Select * from omanik;
select * from loomad;
Loomad Lisamine
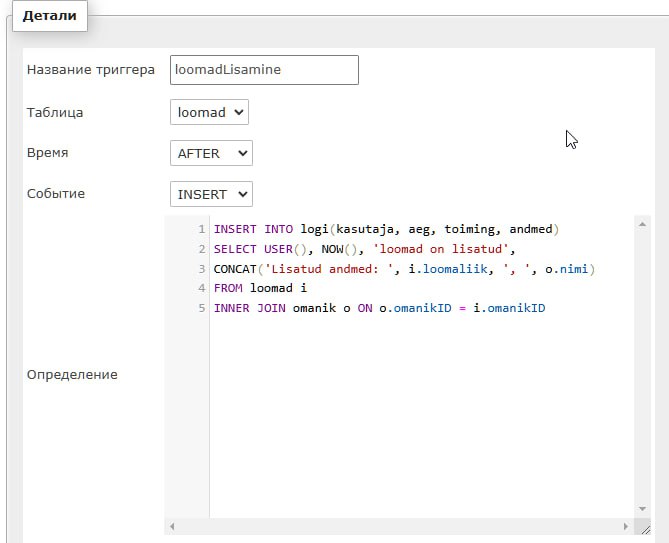
CREATE TRIGGER loomadLisamine
ON loomad
FOR INSERT
AS
INSERT INTO logi(kasutaja, aeg, toiming, andmed)
SELECT USER, GETDATE(), 'loomad on lisatud',
CONCAT(i.loomaliik, ', ', o.nimi)
FROM inserted i
INNER JOIN omanik o
ON o.omanikID = i.omanikID;
--kontrollimiseks
INSERT INTO loomad (loomaliik, nimi, vanus, varv, omanikID)
VALUES ('karu', 'Marta', 3, 'pruun', 1),
('delfiin', 'Roxy', 5, 'sinine', 2),
('kass', 'Murzik', 3, 'punakollane', 1),
('koer', 'Dobi', 4, 'valge', 2);
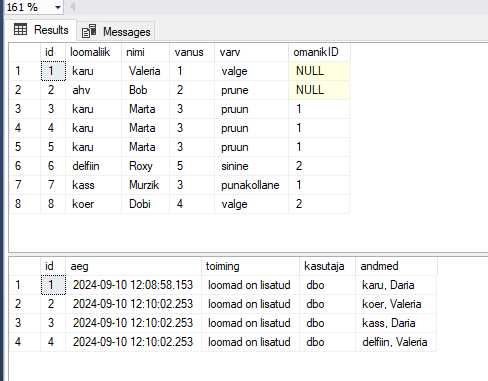
SELECT * FROM loomad;
SELECT * FROM logi;
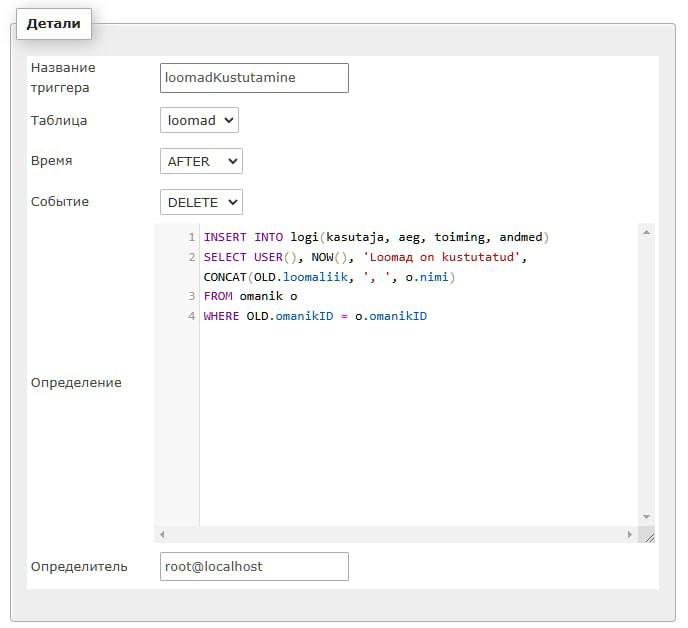
Loomad Kustutamine
create trigger loomadKustutamine
on loomad
for delete
as insert into logi(kasutaja, aeg, toiming, andmed)
select user, getdate(), 'Loomad on kustutatud', concat(deleted.loomaliik, ', ', o.nimi)
from deleted
inner join omanik o
on deleted.omanikID=o.omanikID
--kontroll
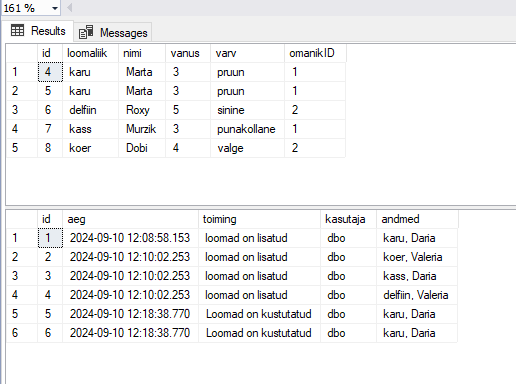
delete from loomad
where id=1;
SELECT * FROM loomad;
SELECT * FROM logi;
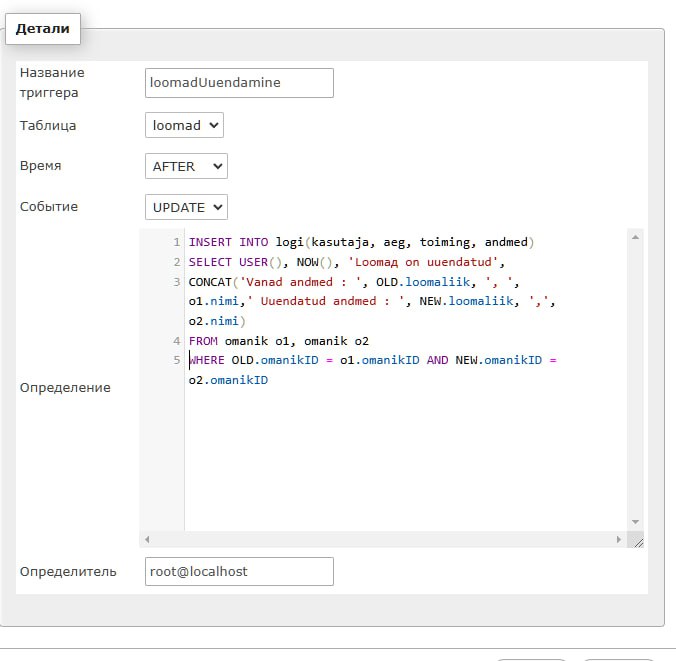
LoomadUuendamine
create trigger loomadUuendamine
on loomad
for update
as
insert into logi(kasutaja, aeg, toiming, andmed)
select user, getdate(), 'Loomad on uuendatud', concat('Vanad andmed : ', deleted.loomaliik, ', ', o1.nimi,
'Uuendanud andmed : ', inserted.loomaliik, ', ', o2.nimi)
from deleted
inner join inserted on deleted.id=inserted.id
inner join omanik o1 on deleted.omanikID=o1.omanikID
inner join omanik o2 on inserted.omanikID=o2.omanikID;
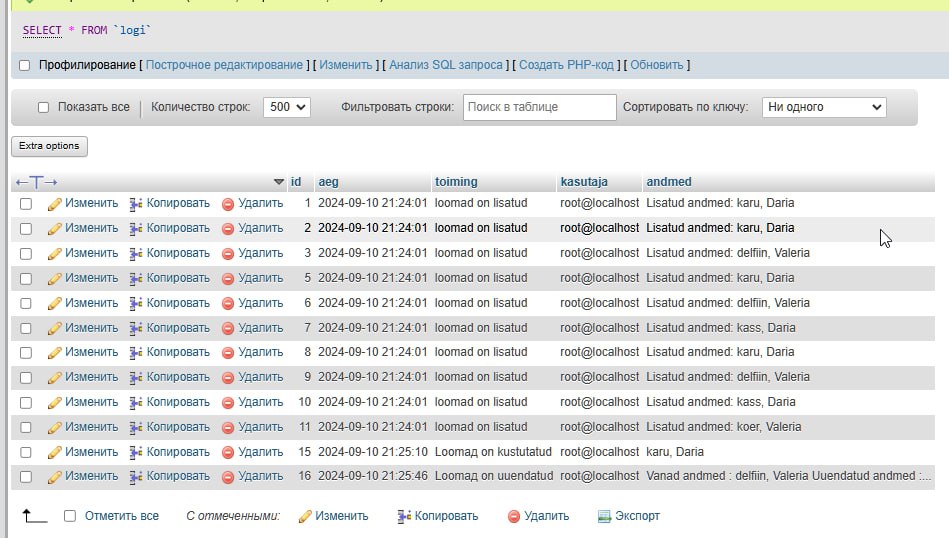
update loomad set loomaliik='jänes', omanikID=5
where id=5;
select * from loomad;
select * from logi;
XAMPP Trigerid kahe seotud tabelite põhjal
Loomad Lisamine
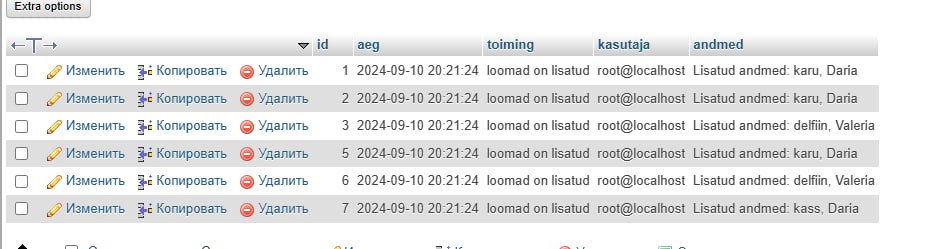
Loomad Kustutamine
LoomadUuendamine